ICS - Arch Lab | 处理器太慢怎么办?
Last updated on December 17, 2025 am
在 Arch Lab 中,我们将熟悉流水线 Y86-64 处理器的设计与实现,并对该处理器及一个基准测试程序进行优化,以实现性能最大化。实验分为三个部分:
- Part A:编写一些简单的 Y86-64 程序,并熟悉 Y86-64 相关工具的使用。
- Part B:为 SEQ 模拟器扩展新的指令并完善 CPU 流水线的实现过程。
- Part C:对 Y86-64 基准测试程序及其架构设计进行优化。
预备知识
Y86-64 指令集架构
Y86-64 是基于 x86-64 简化而来的指令集,定义了指令格式、寄存器组、寻址方式及程序状态码,是 Arch Lab 中处理器设计的指令规范。
HCL 硬件描述语言
HCL 是用于描述硬件逻辑的简化语言,重点支持组合逻辑与时序逻辑表达,是实现处理器模拟器控制逻辑的核心工具。
SEQ 架构
SEQ 是基础的单周期处理器架构,每条指令的取指、译码、执行等阶段串行完成,是理解流水线架构的基础模型。
PIPE 架构
PIPE 是将指令执行拆解为多个流水线阶段并行处理的架构,可提升指令吞吐量,需解决数据冒险、控制冒险等关键问题。
前置准备
环境配置
参考指导文档进行环境配置。
1 | |
在每次更改 Rust 源码后,应重新构建项目。
1 | |
工具集
构建项目后,将产生一个 archlab-project/target 文件夹来存储输出的二进制文件和其他中间文件。输出的可执行文件是:
- Y86-64 汇编器:target/debug/yas
- Y86-64 调试器:target/debug/ydb
- Y86-64 ISA 模拟器:target/debug/yis
- Y86-64 流水线模拟器:target/debug/ysim
- 本地评分器:target/debug/grader
可通过以下命令启动本地评分器:
1 | |
其余工具详情可参看 archlab-project/README.md。
git init
为了便于管理代码版本,笔者建议在 archlab-project 目录下初始化一个 Git 仓库:
1 | |
用于追踪代码变更。
Part A
Part A 中,我们将在 archlab-project/misc 目录下开展工作。我们的任务是编写三个 Y86-64 程序实现三个函数。
sum.ys
参照给出的示例代码:
1 | |
这是一段链表的求和函数,我们可以在 sum.ys 中编写如下 Y86-64 程序:
1 | |
rsum.ys
参照给出的示例代码:
1 | |
这是一段链表的递归求和函数,我们可以在 rsum.ys 中编写如下 Y86-64 程序:
1 | |
bubble.ys
参照给出的示例代码:
1 | |
这是一段冒泡排序函数,我们可以在 bubble.ys 中编写如下 Y86-64 程序:
1 | |
Part B
Part B 中,我们将在 archlab-project/sim/src/architectures/extra 目录下开展工作。我们的任务是逐步完善一系列处理器架构。它们均使用 HCL 语言描述,我们只需修改相应的占位符为正确的表达式。占位符一共有三种:
- BOOL_PLACEHOLDER
- U8_PLACEHOLDER
- U64_PLACEHOLDER
seq_full.rs
在 seq_full.rs 中,我们需要扩展 SEQ 处理器以支持以下指令:
- iopq V, rB
Fetch 阶段,需要保证 IOPQ 是一条有效指令,需要读取寄存器和立即数。
1 | |
Decode 阶段,与 OPQ 指令类似,需要将 rB 设置为 srcB 从寄存器文件中取值,并将写入地址 dstE 设置为 rB。
1 | |
Execute 阶段,需要指定 ALU 的输入,并更新条件码。
1 | |
其余阶段无需调整。
pipe_s3a.rs
在 pipe_s3a.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s2.rs 的基础上进一步优化。我们发现 pipe_s2 的关键路径长度为 7,而计算 f_pc 的依赖路径过长。为了减少 f_pc 的依赖路径长度,我们进一步拆分了流水线阶段,将解码阶段与随后执行、存储和写回阶段分开。然而,这样做引入了新的问题:
reg_read和reg_write现在位于不同的流水线阶段,这可能导致数据冒险。用于计算
f_pc的操作数也被拆分到不同的流水线阶段,这实际上是不正确的,因为在特定时间点位于不同流水线阶段的值属于不同的指令。
为了解决上述问题,我们在必要时对流水线寄存器实施阻塞或冒泡控制,确保等待一个额外的周期以保证计算结果的正确性。
pipe_s3a.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s3b.rs
在 pipe_s3b.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s3a.rs 的基础上进一步优化。pipe_s3a 的一个问题是停顿和气泡的频率太高,这实际上降低了性能。除了使用停顿和气泡来处理数据冒险之外,也可以通过转发来解决。
pipe_s3b.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s3c.rs
在 pipe_s3c.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s3b.rs 的基础上进一步优化。pipe_s3b 的性能提升不是很显著,因为当遇到 JX 指令时,我们总是会停顿/产生气泡。实际上,我们在解码阶段就已知两种分支选项,只是必须等到执行阶段才能确定选择哪条分支,我们可以基于此实现分支预测。
pipe_s3c.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s3d.rs
在 pipe_s3d.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s3c.rs 的基础上进一步优化。从 pipe_s3c 到 pipe_s3d 的主要变化在于硬件设计。我们将寄存器读取和写入合并到一个名为 reg_file 的设备中,操作顺序为先写后读。此更改的目的是为了避免结构风险。
pipe_s3d.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s4a.rs
在 pipe_s4a.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s3d.rs 的基础上进一步优化。为了进一步减少计算依赖层级,我们已经将执行阶段与其他阶段分离。实际上,通过在 pipe_s3d 中强制对寄存器执行先写后读的顺序,我们可以避免可能在 pipe_s4 中发生的结构性冒险。
pipe_s4a.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s4b.rs
在 pipe_s4b.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s4a.rs 的基础上进一步优化。我们注意到用于计算 f_pc 的 e_cnd 的依赖路径太长。因此,我们可以将 e_cnd 存储在存储阶段寄存器中,并用 M.cnd 替代它。
pipe_s4b.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
pipe_s4c.rs
在 pipe_s4c.rs 中,我们需要在 pipe_s4b.rs 的基础上进一步优化。类似于 pipe_std.rs,我们在解码阶段将 D.valP 输入到 d_valA 中,以消除执行和存储阶段流水线寄存器中的 valP。
pipe_s4c.rs 的占位符修改如下:
1 | |
Part C
Part C 中,我们将在 archlab-project/misc 和 archlab-project/sim/src/architectures/extra 目录下开展工作。我们的任务是修改 archlab-project/misc/ncopy.ys 和 archlab-project/sim/src/architectures/extra/ncopy.rs,让 ncopy 运行得尽可能快。最终性能将根据 cpe 和 ac 来评估。
- cpe (cycles per element):如果模拟代码需要 C 个周期来复制一个包含 N 个元素的块,那么 CPE 就是 C/N。
- ac (architecture cost):ncopy 架构的关键路径长度。形式上,CPU 架构的关键路径是时钟元件之间组合逻辑的最长路径。关键路径的长度可以用来衡量 CPU 的时钟频率,从而用于估算架构性能。在 Part C 中,关键路径的长度简化为:1 加上在架构路径中排列的硬件设备(单元)的最大数量。
ncopy 的 C 语言描述在 misc/ncopy.c 中。ncopy 函数将一个长度为 len 的整数数组 src 复制到一个不重叠的 dst 中,并返回 src 中正整数的数量。
1 | |
应用 PIPE 架构
由于 ncopy.rs 初始是 SEQ 架构,我们用 archlab-project/sim/src/architectures/builtin/pipe_std.rs 的内容完整替换 ncopy.rs 文件的内容。初步优化处理器架构,减少 ac。
添加 IOPQ 指令
查看 ncopy.ys 中的初始汇编代码。
1 | |
发现每次进行 count++ 时,都需要先 irmovq 将立即数 1 加载到寄存器中,然后再进行加法操作。我们可以使用 IOPQ 指令来直接将立即数与寄存器相加,从而减少指令数量和执行时间。为此,我们需要在 ncopy.rs 中添加 IOPQ 指令。具体步骤可参考 Part B 部分针对 seq_full.rs 的修改。
循环展开
至此,我们已经将架构从 SEQ 升级到了 PIPE,并通过 IOPQ 指令减少了指令数量。进一步观察发现,每一次循环最后都需要经历一次条件跳转,这意味着每次循环都要经历控制冒险,但却只处理了一个元素。我们可以通过循环展开,在一次循环中处理多个元素来进一步提升 cpe。
循环展开参考代码如下:
1 | |
余数二分处理
循环展开带来的问题是当 len 不是展开倍数时,剩余的元素无法通过展开后的循环处理。为了解决这个问题,我们需要针对不同的余数情况编写不同的处理代码,形成类似跳转表的结构。为了避免代码重复和过多的跳转,我们可以针对每个剩余的元素编写处理代码,Rk 对应对第 k 个剩余元素的处理,然后将这些代码块按照从大到小串联起来。对于不同的余数情况,我们只需要跳转到对应的 Rk 代码块即可,程序会顺序执行后续的对第 k-1、k-2、…、1 个剩余元素的处理代码。
余数处理参考代码如下:
1 | |
注意这里将 andq 指令插入到 mrmovq 和 rmmovq 之间,从而避免了流水线暂停。
至于跳转部分,我们可以对余数反复减一并判断是否为零来跳转到对应的代码块。也可以选择使用二分思想来减少跳转次数。
完整 ncopy.ys 参考代码如下:
1 | |
减少关键路径长度
目前我们的 ncopy.rs 采用的是 PIPE 架构,关键路径长度为 4,正是执行阶段 e_cnd 的依赖路径。
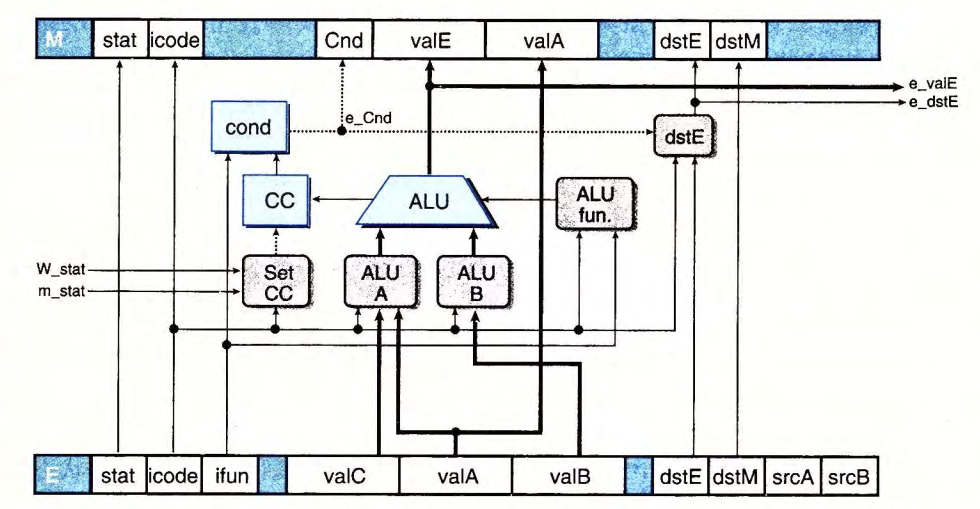
回忆 dstE 需要 e_cnd 更新的情况,为条件传送 CMOVX 指令。而 CMOVX 指令并不更新条件码。由此可知,更新条件码和需要计算 e_cnd 更新 dstE 的情况不会在执行阶段同时发生。因此,我们可以在执行阶段寄存器中新增 pre_cc 记录上一条指令的条件码,用于通过 cond 单元计算 e_cnd,从而降低关键路径长度为 3。
ncopy.rs 参考修改如下:
1 | |
更适合北大宝宝体质的 Arch Lab 踩坑记
CSAPP - archlab
Introduction-to-Computer-Systems-2025Fall-PKU